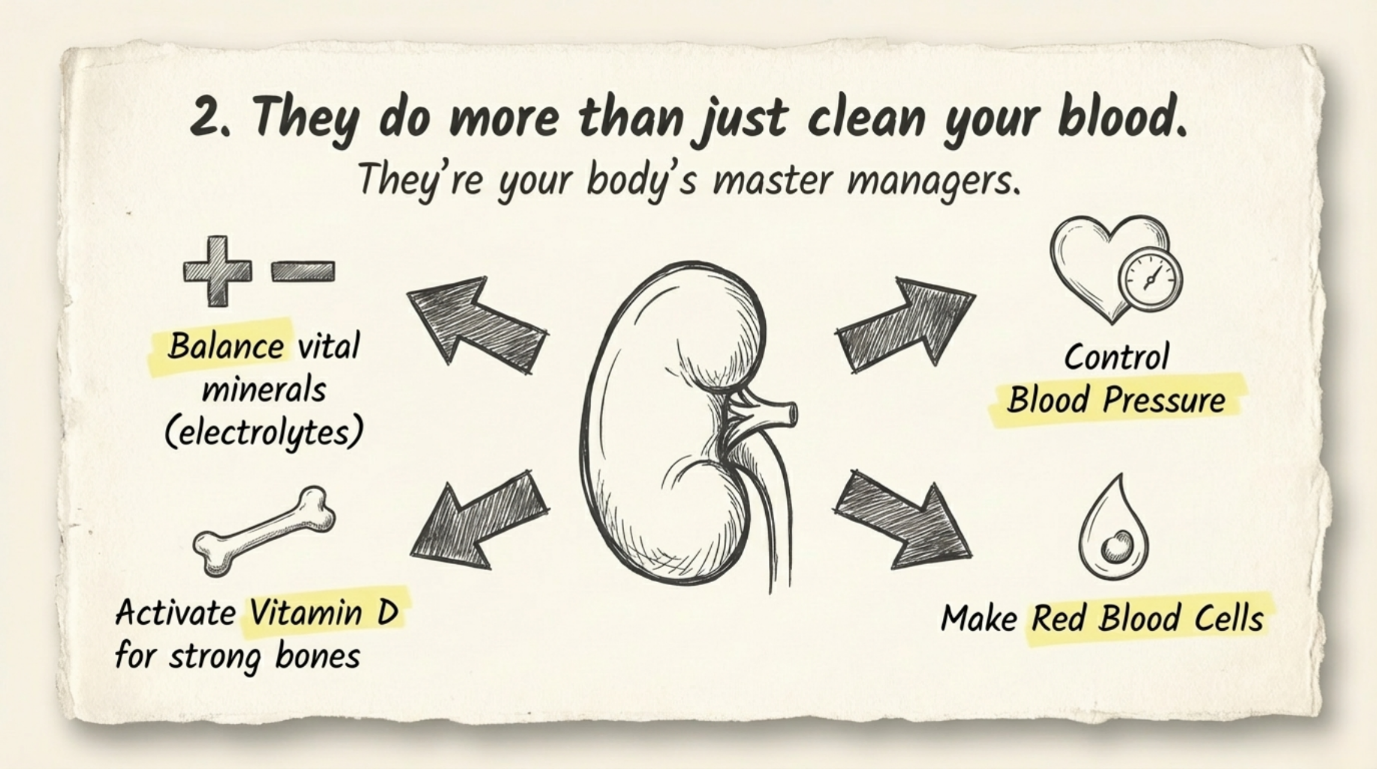
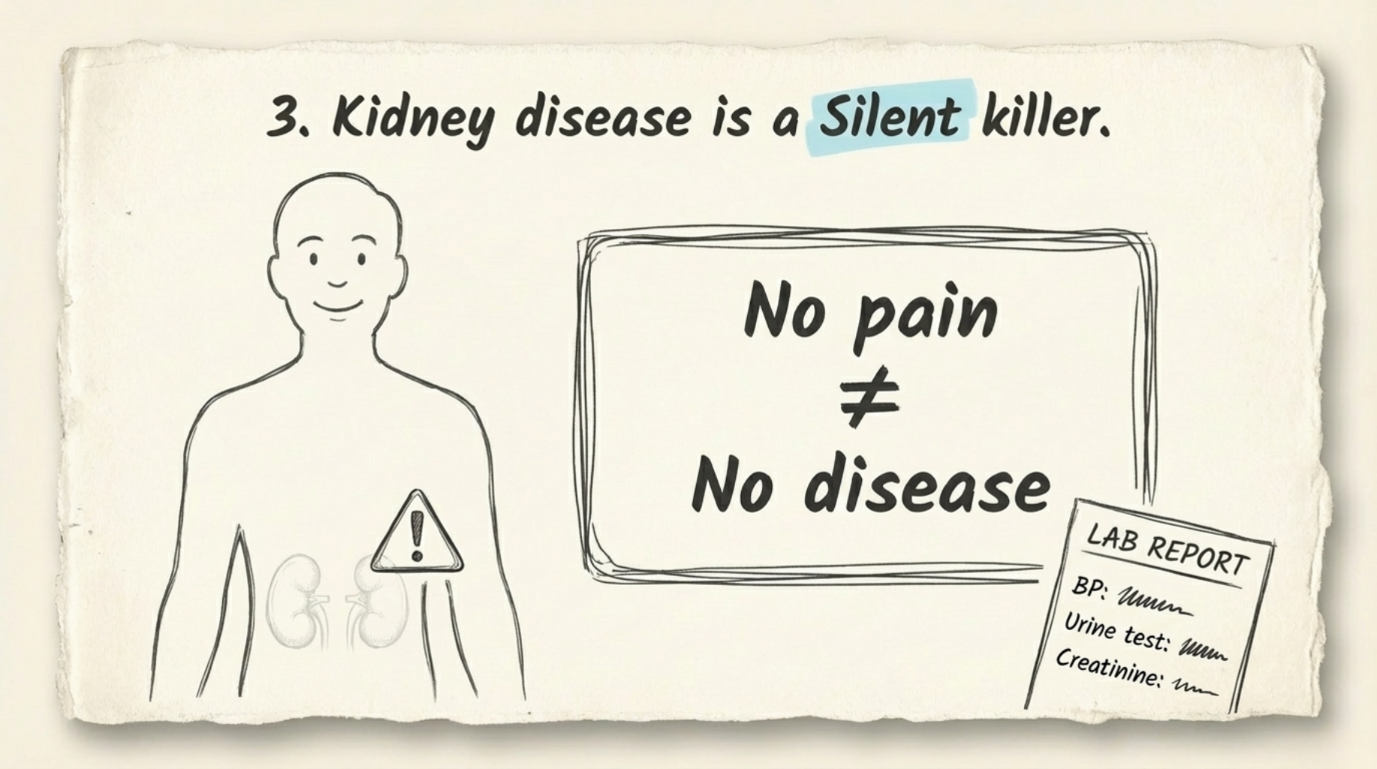
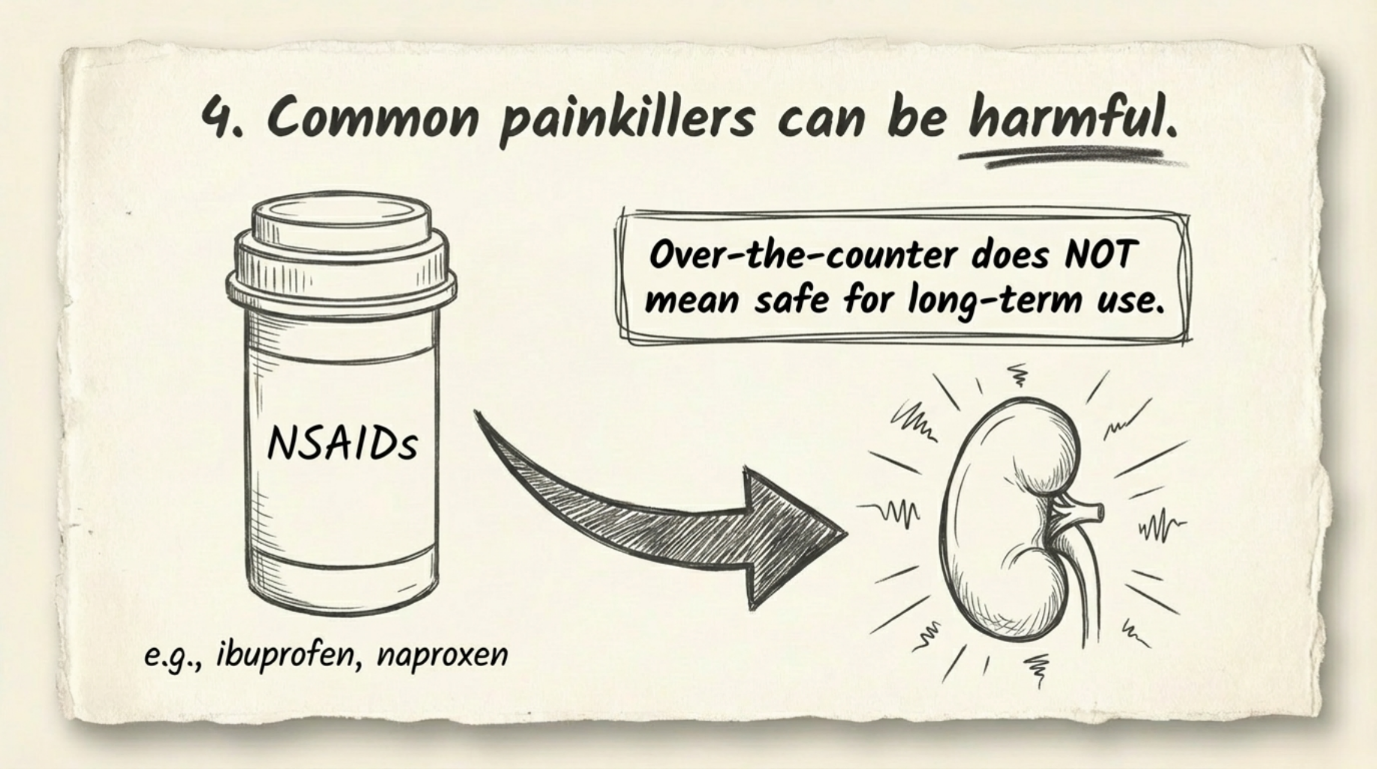
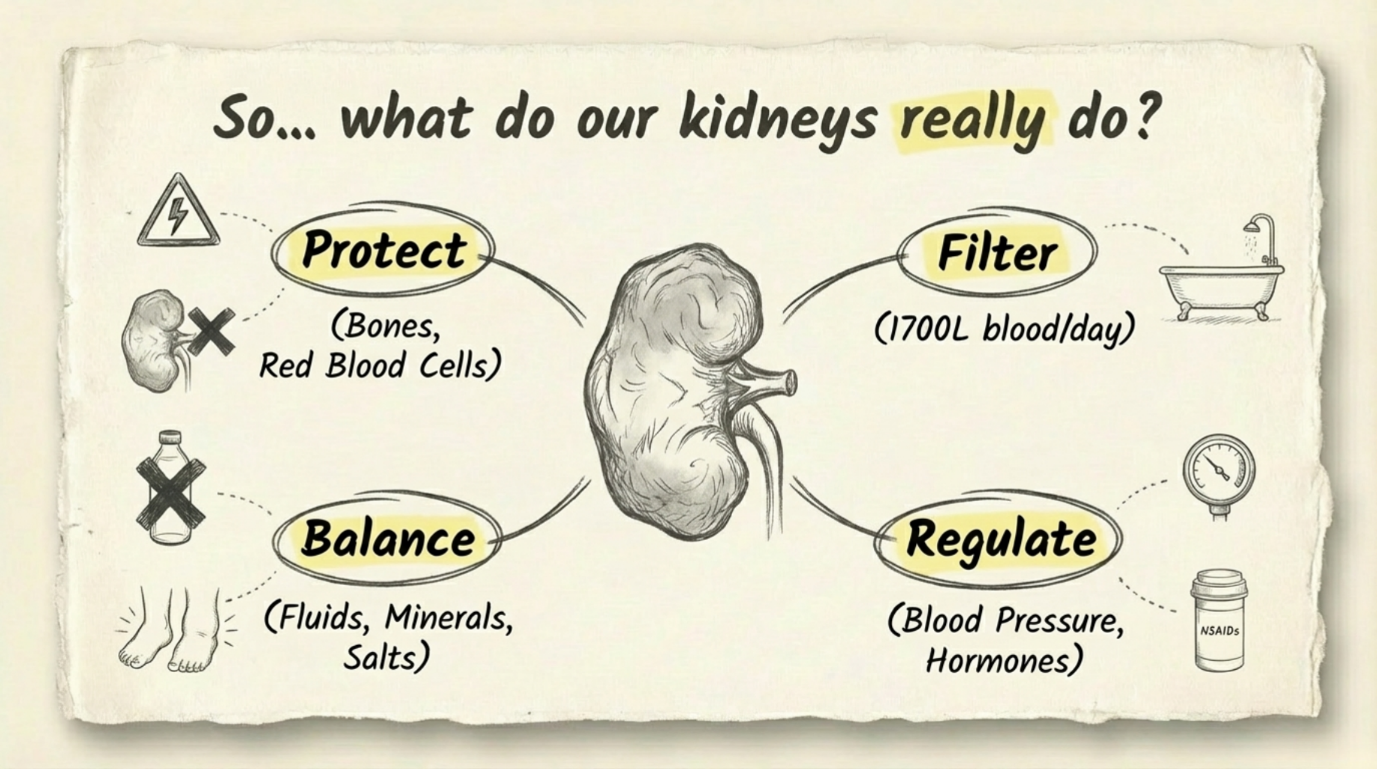
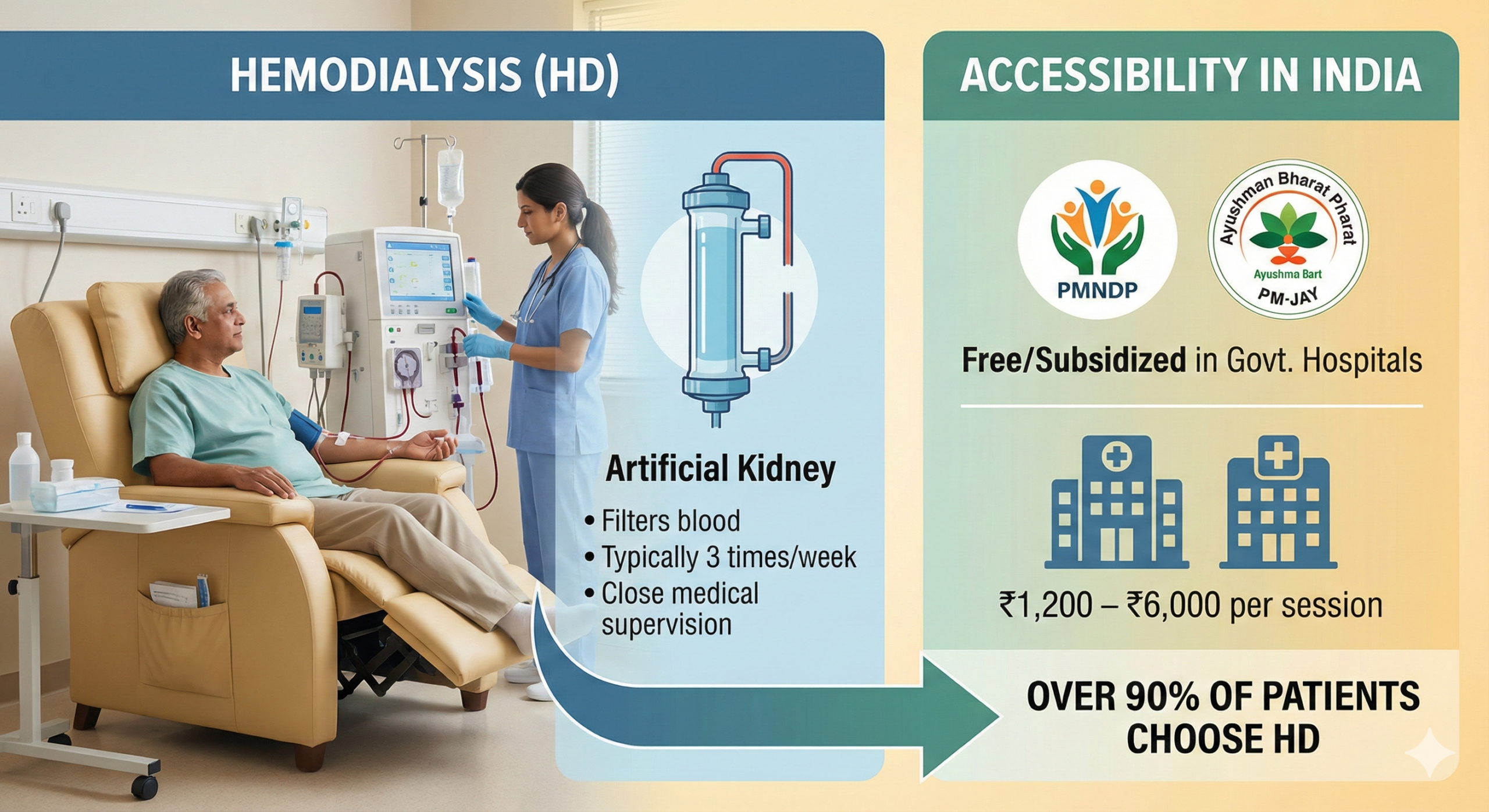
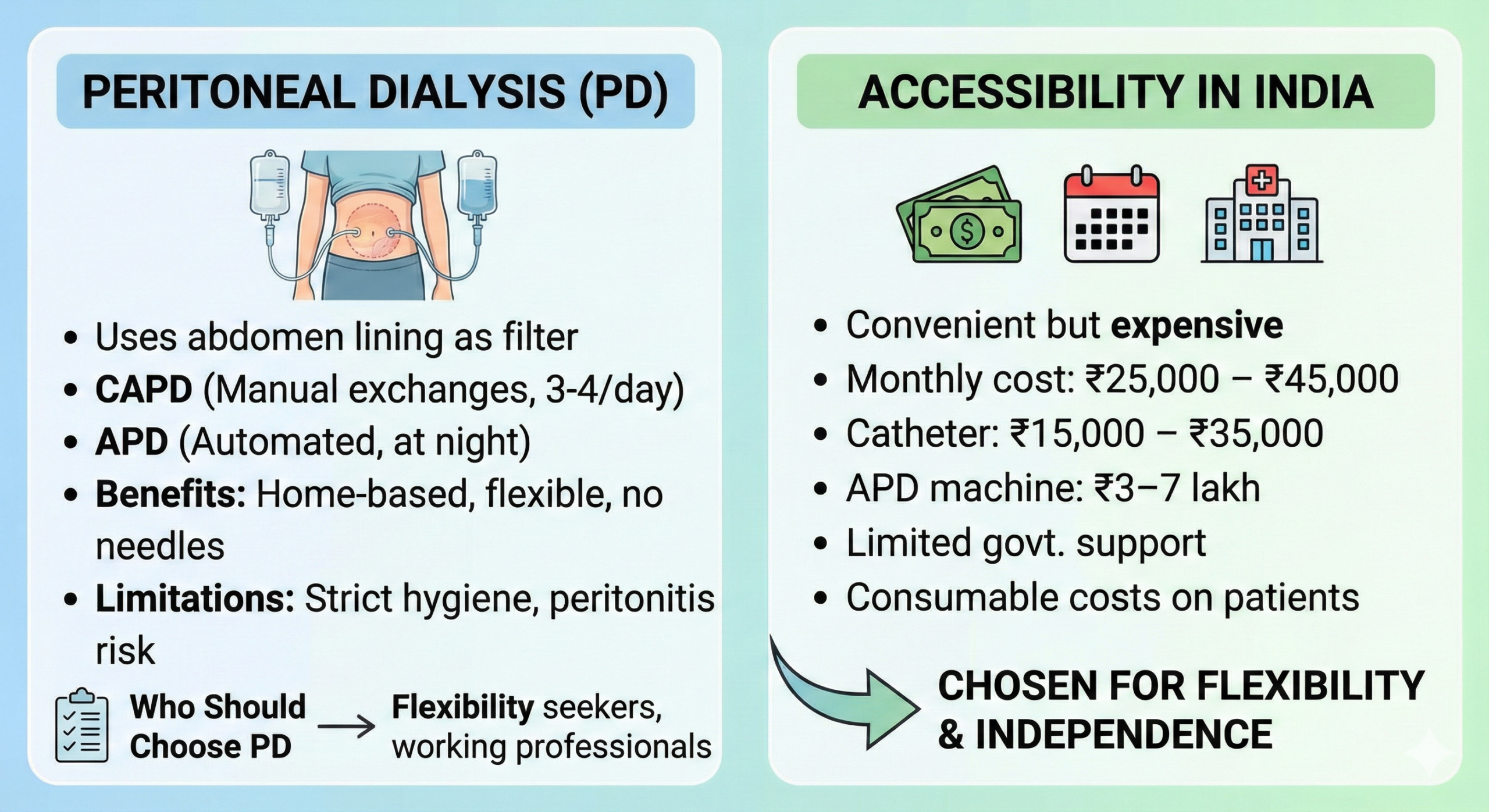
Kidney stones are a common health problem that can affect people of any age. They form when minerals and salts in the urine stick together and become hard deposits inside the kidneys. The symptoms, treatment, and chances of getting stones again depend on the size, type, and location of the stone, as well as your overall health. Understanding treatment options and prevention methods helps keep your kidneys healthy in the long run.
What Causes Kidney Stones?
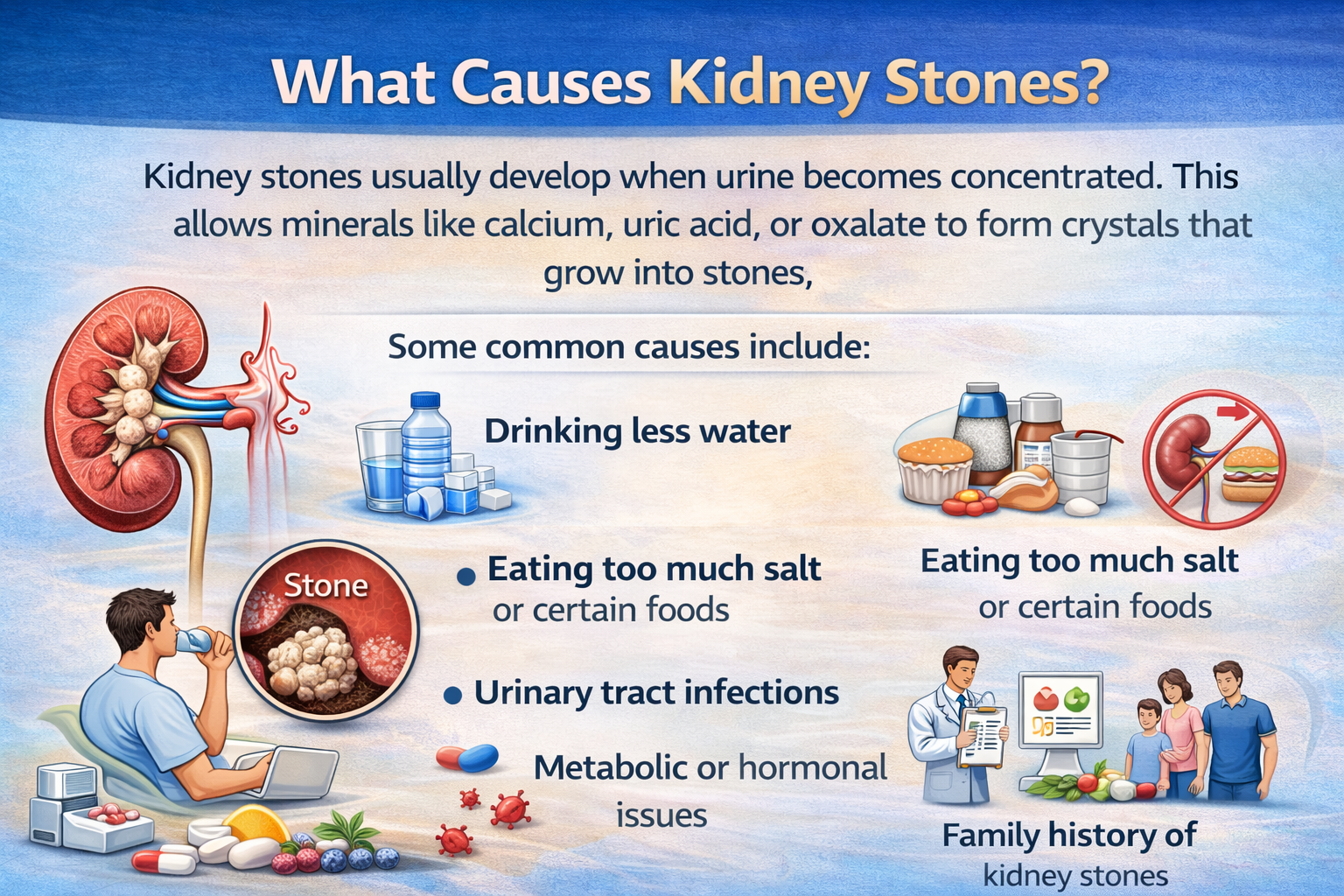
Kidney stones usually develop when urine becomes concentrated. This allows minerals like calcium, uric acid, or oxalate to form crystals that grow into stones.
Some common causes include:
- Drinking less water
- Eating too much salt or certain foods
- Urinary tract infections
- Metabolic or hormonal issues
- Family history of kidney stones
Some people get stones only once, while others may experience them repeatedly. Dehydration, high calcium in urine, or certain health conditions can increase the risk. Stones can stay silent for years, but when they move, they often cause severe pain.
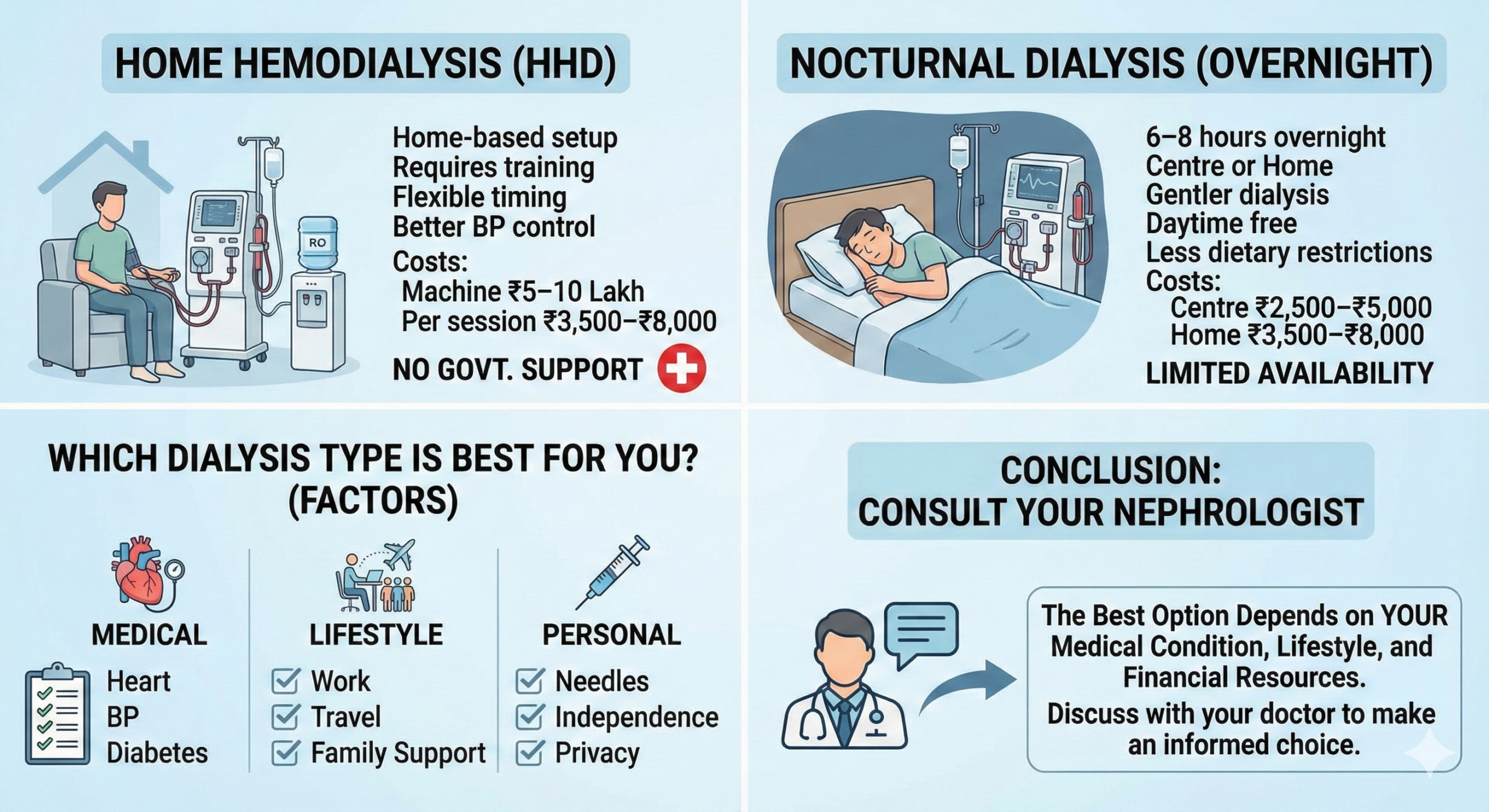
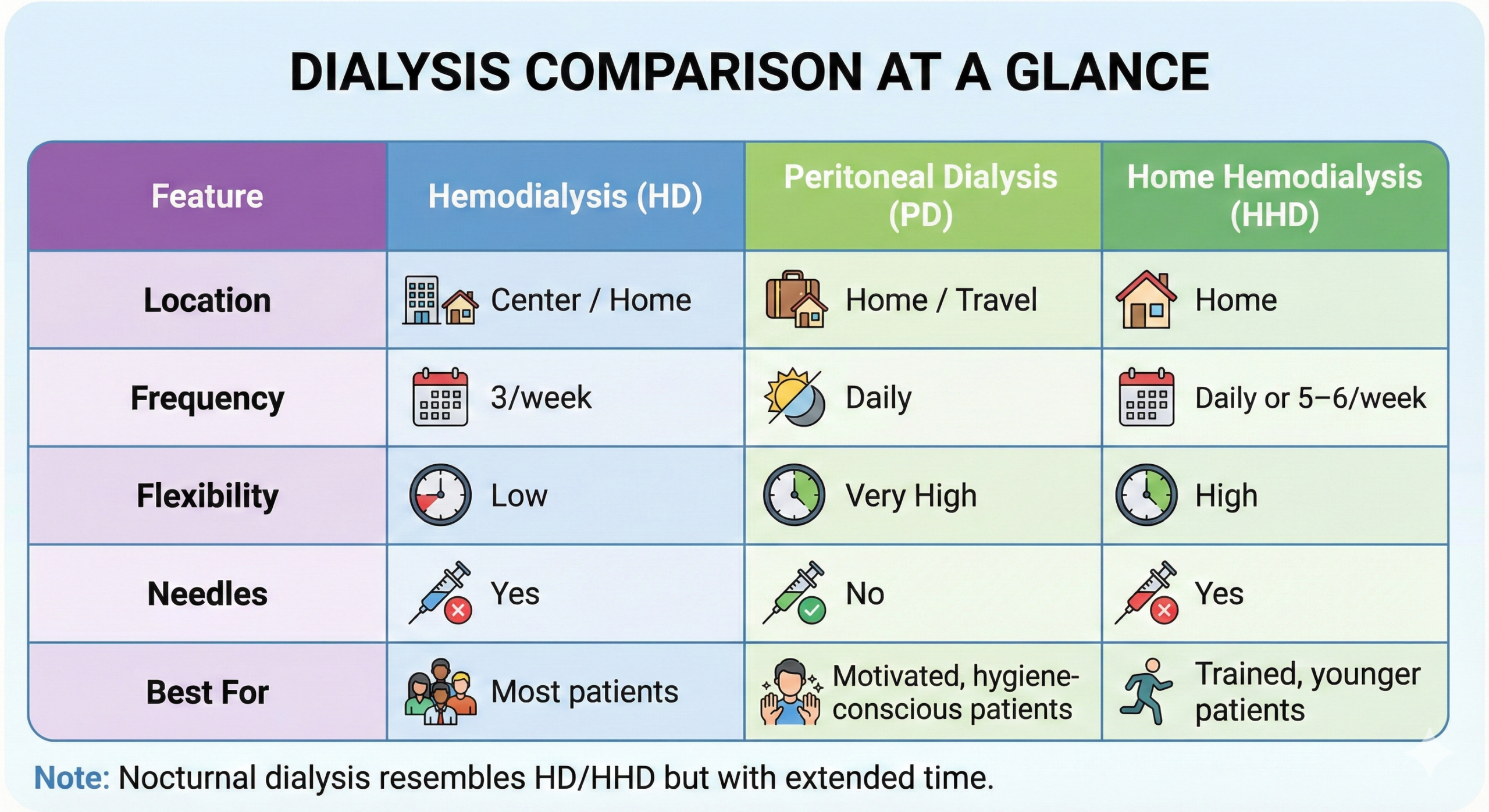
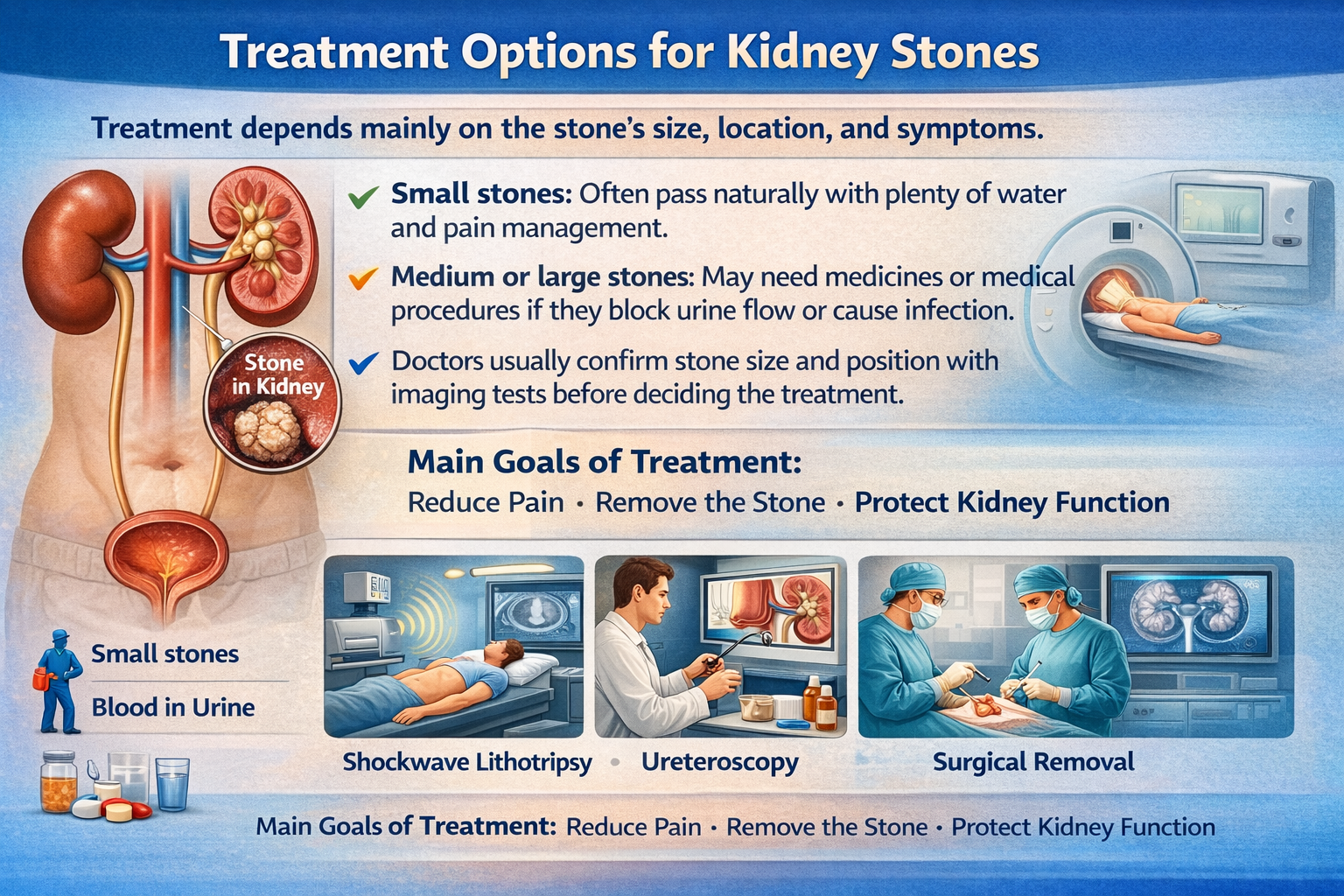
Treatment Options for Kidney Stones
Treatment depends mainly on the stone’s size, location, and symptoms.
- Small stones: Often pass naturally with plenty of water and pain management.
- Medium or large stones: May need medicines or medical procedures if they block urine flow or cause infection.
- Doctors usually confirm stone size and position with imaging tests before deciding the treatment.
The main goals of treatment are simple — reduce pain, remove the stone, and protect kidney function.
Medicines Used for Kidney Stones
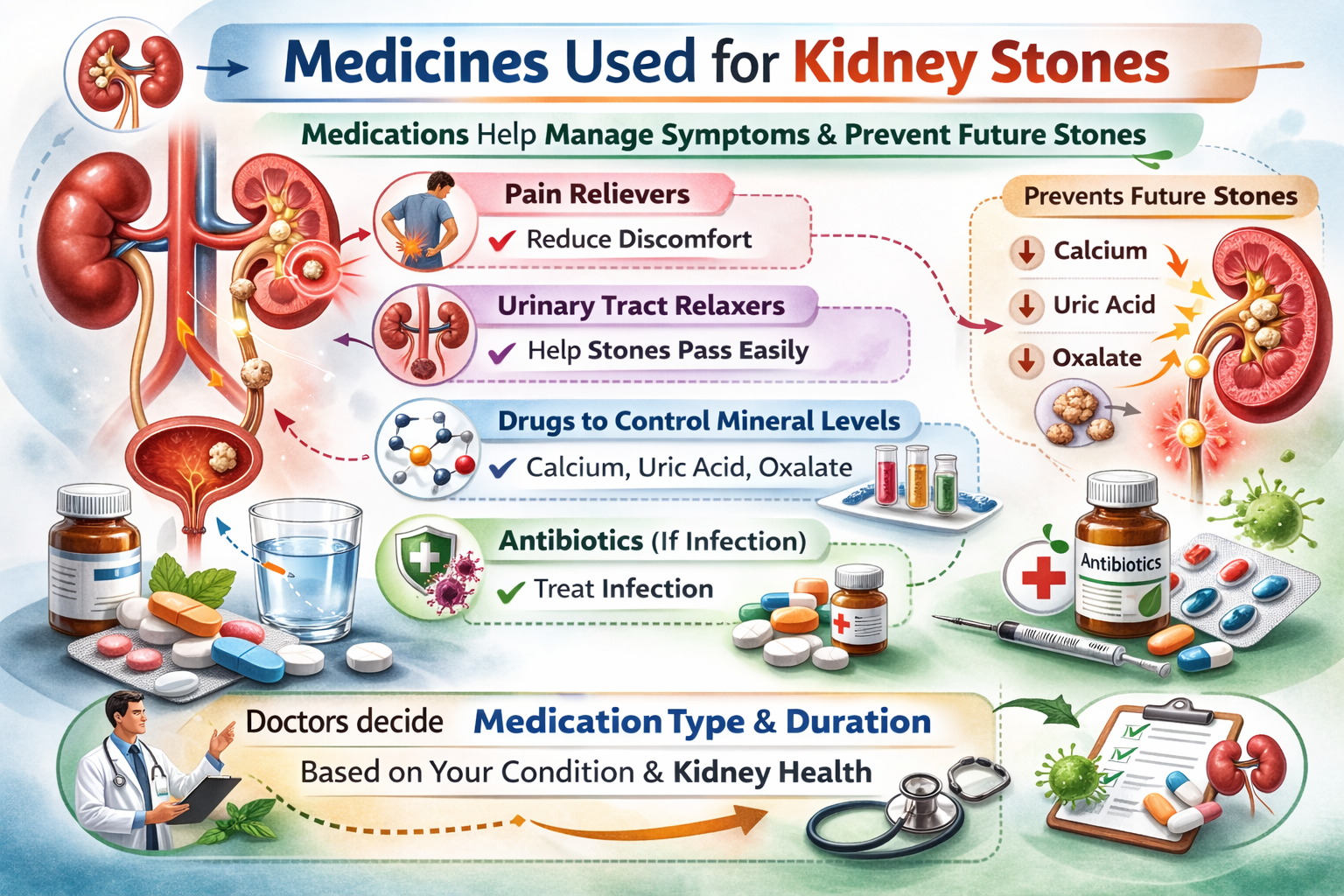
Medications are often used to help manage symptoms and prevent future stones:
- Pain relievers to reduce discomfort
- Medicines that relax the urinary tract to help stones pass easily
- Drugs that control calcium, uric acid, or oxalate levels
- Antibiotics if infection is present
Doctors decide the medication type and duration based on your condition and kidney health.
Diet Changes to Prevent Kidney Stones

Diet plays a big role in preventing kidney stones. Many people focus only on treatment but ignore daily eating habits.
Here are some simple preventive steps:
- Drink plenty of water daily
- Reduce salt intake
- Eat balanced meals with fruits and vegetables
- Avoid excessive processed foods
- Follow portion control if you have kidney issues
While certain fruits help hydration and digestion, they don’t dissolve stones but support overall kidney health.
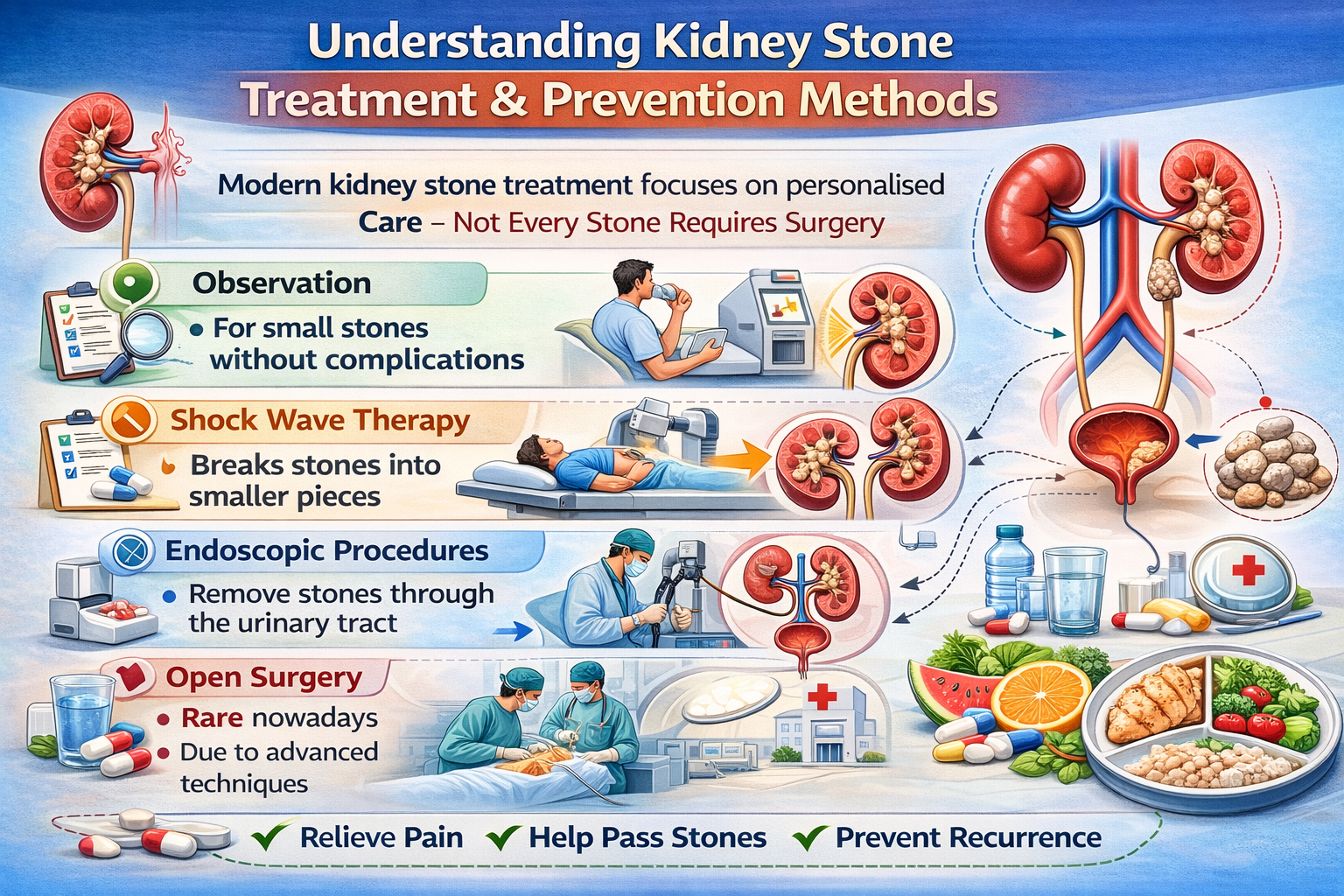
Latest Treatment Approaches
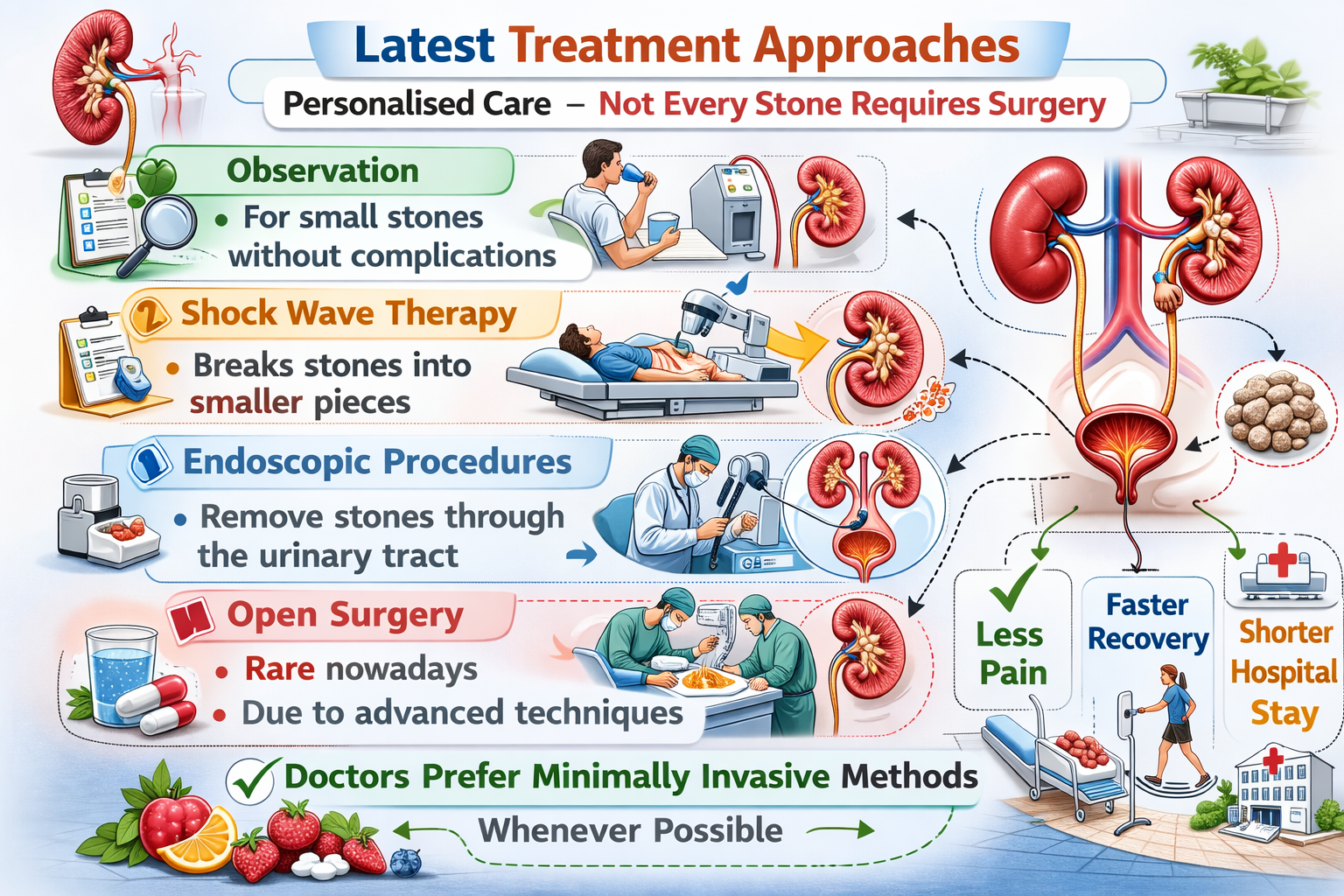
Modern kidney stone treatment focuses on personalised care. Not every stone requires surgery.
Common approaches include:
- Observation: For small stones without complications
- Shock wave therapy: Breaks stones into smaller pieces
- Endoscopic procedures: Remove stones through the urinary tract
- Open surgery: Rare nowadays due to advanced techniques
Doctors usually choose minimally invasive methods whenever possible.
Conclusion
Kidney stones can cause severe pain, but effective treatments are available. From medicines to advanced procedures, treatment focuses on relief and protecting kidney health. Prevention mainly depends on simple daily habits like staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and regular medical check-ups.
People who frequently get stones or have kidney problems should consult a kidney specialist for proper evaluation and long-term prevention. Expert guidance helps identify the stone type, risk factors, and the best prevention plan.